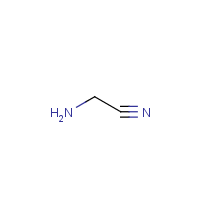
Aminoacetonitrile is the organic compound with the formula H2N−CH2−C≡N. The compound is a colorless liquid. It is unstable at room temperature, owing to the incompatibility of the amine nucleophile and the nitrile electrophile. For this reason it is usually encountered as the chloride and bisulfate salts of the ammonium derivative, i.e., [NCCH2NH3] Cl− and [NCCH2NH3] HSO4−.
Production and applications
Industrially aminoacetonitrile is produced from glycolonitrile by reaction with ammonia:
- HOCH2CN NH3 → H2NCH2CN H2O
The aminoacetonitrile can be hydrolysed to give glycine: Being bifunctional, it is useful in the synthesis of diverse nitrogen-containing heterocycles.
Aminoacetonitrile derivatives are useful antihelmintics. They act as nematode specific ACh agonists causing a spastic paralysis and rapid expulsion from the host.
Occurrence in the interstellar medium
Using radio astronomy, aminoacetonitrile was discovered in the Large Molecule Heimat, a giant gas cloud near the Galactic Center in the constellation Sagittarius. This discovery is significant to the debate on whether glycine exists widely in the universe.
References
External links
- Property data at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)